
Training people with aphasia
to use compensatory writing
software for email writing
Dr Paul Conroy
Dr Lindsey Thiel

Aphasia and the internet
Recent survey study by Menger, Morris & Salis (2014):
• PWA use the internet less than people with stroke and
no aphasia
• Only 22% of PWA aphasia rated their own internet skills
as good or excellent, compared to 74% of UK
population (OXIS, 2010)
• Main barrier to using the internet in PWA was their
aphasia
• Most popular type of internet use in internet users with
aphasia was email, but 71% needed help with this

Writing therapy studies
Recent review (Thiel, Sage & Conroy, 2015)
found 62 writing therapy studies
– 54 evaluated impairment-based therapies
e.g. Ball, de Riesthal, Breeding, & Mendoza (2011)
Beeson, Higginson & Rising (2013) Tsapkini & Hillis (2013)
– 13 of these trained functional writing skills
e.g. Mortley, Enderby and Petheram (2001) Robson,
Marshall, Chiat, & Pring (2001) Panton & Marshall (2008)
– 3 trained writing for the internet or mobile phones
Beeson et al. (2002), Beeson et al (2013) (Greenwald,
2004)

Writing therapy studies
• 14 evaluated assistive technologies for writing
• Included
– electronic spelling aid (Beeson, Rising, Kim, & Rapcsak, 2010),
– Lightwriter (Jackson-Waite, Robson, & Pring, 2003)
– predictive writing software (Behrns et al., 2009)
– voice recognition software (Estes & Bloom, 2011)
– C-Speak Aphasia (Nicholas et al., 2011)
– speech synthesiser software (Armstrong & Macdonald, 2000)
• 3 trained writing for the internet (Estes & Bloom, 2011;
Nicholas et al., 2005; Nicholas et al., 2011)
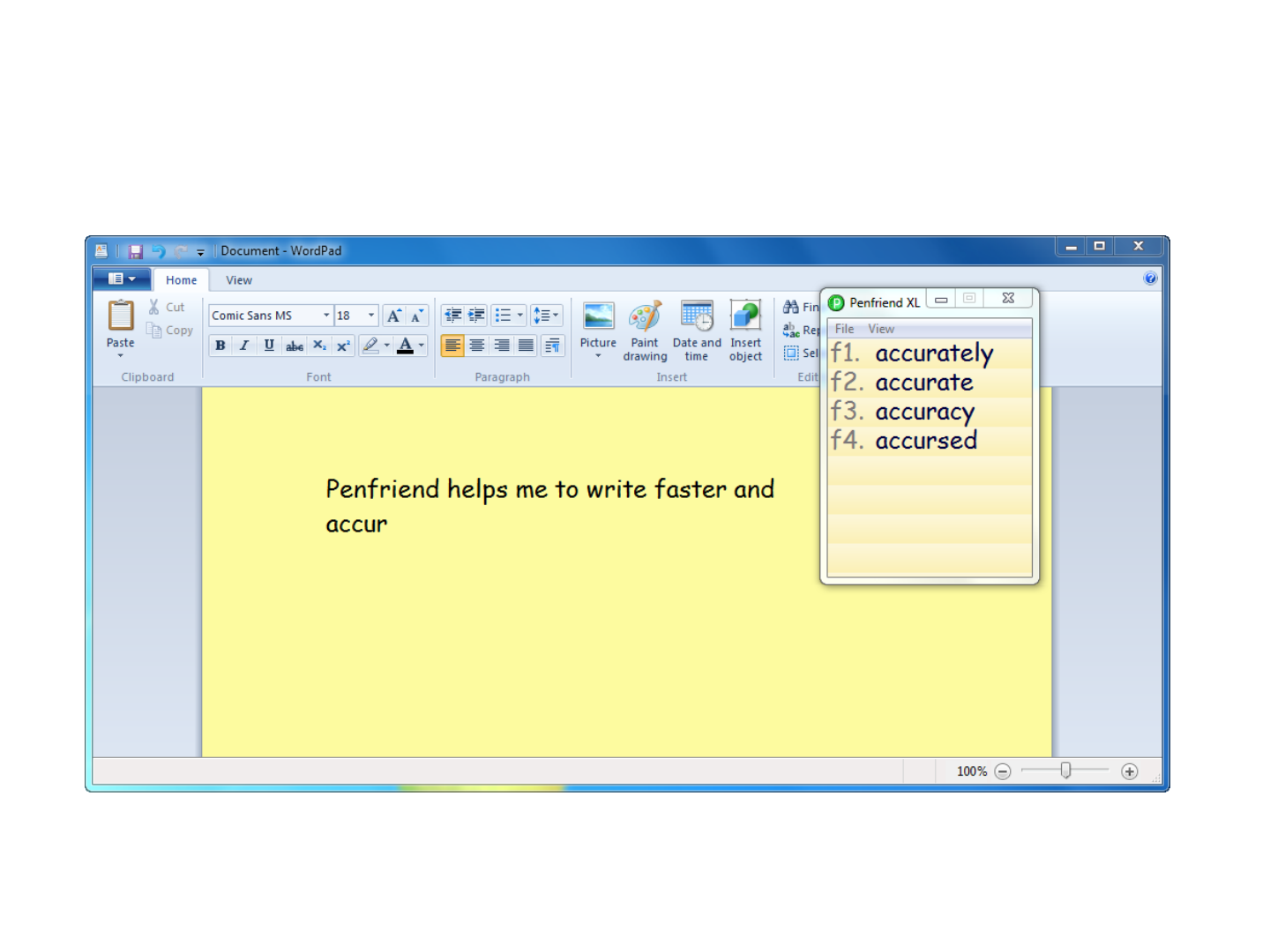
Our focus: predictive & editing writing software
Penfriend Ltd.

Predictive writing software
• Designed to assist people with physical disabilities with
writing (e.g. Higginbotham, 1992)
• Also used with children with developmental language or
learning disabilities (e.g. MacArthur 1996)
• Studies with aphasia
– Armstrong & Macdonald, 2000
– Behrns et al., 2009
– Mortley et al., 2001
– Murray & Karcher, 2000
• Changes to written texts such as increased length and
accuracy or richer in terms of content

Motivations for study
• People with aphasia are often excluded from using the
internet due to their aphasia
• Access to internet could mean more opportunities for
communication and better access to information for PWA
• Lack of therapy studies measuring functional outcomes of
writing therapies
• What is the potential of predictive writing software to
improve writing in terms of
spelling accuracy and speed?

Outcome measures
• Functional writing (email) task
• Frequency diary
• Written picture description
• CAT disability questionnaire
• Computer and internet skills
• Keyboard skills
• Self-correction of spelling
• Interviews

Functional writing task
1. Write an email arranging to meet a friend at a
certain time, place and date.
2. Write an email to a friend telling them about a
recent holiday.
3. Write an email to your MP about an issue of
concern to you at the present time
Functional writing task
• Participants completed at following time points:
• Each email timed and 3 minute cut off
• All video-recorded
• Discourse analysis measures:
– Number of units
– Number of correct units
– Number of correct and informative content words
With
out Co:Writer
With
Co:Writer
Pre
effort phase
Post effort phase
Post therapy
6 month
follow-up
Control participants
10 healthy control participants
Healthy controls
PWA
Age
Mean
62.1
60.4
SD
11.1
12.0
Education
Mean
12.1
11.3
SD
2.2
2.1
Control data
Items
Correct items
Correct and
informative
items
Mean
174.5
173.1
101
SD
94.9
94.9
56.7
• Each completed email writing task
• Maximum 3 minutes per email
• Data for combined tasks:
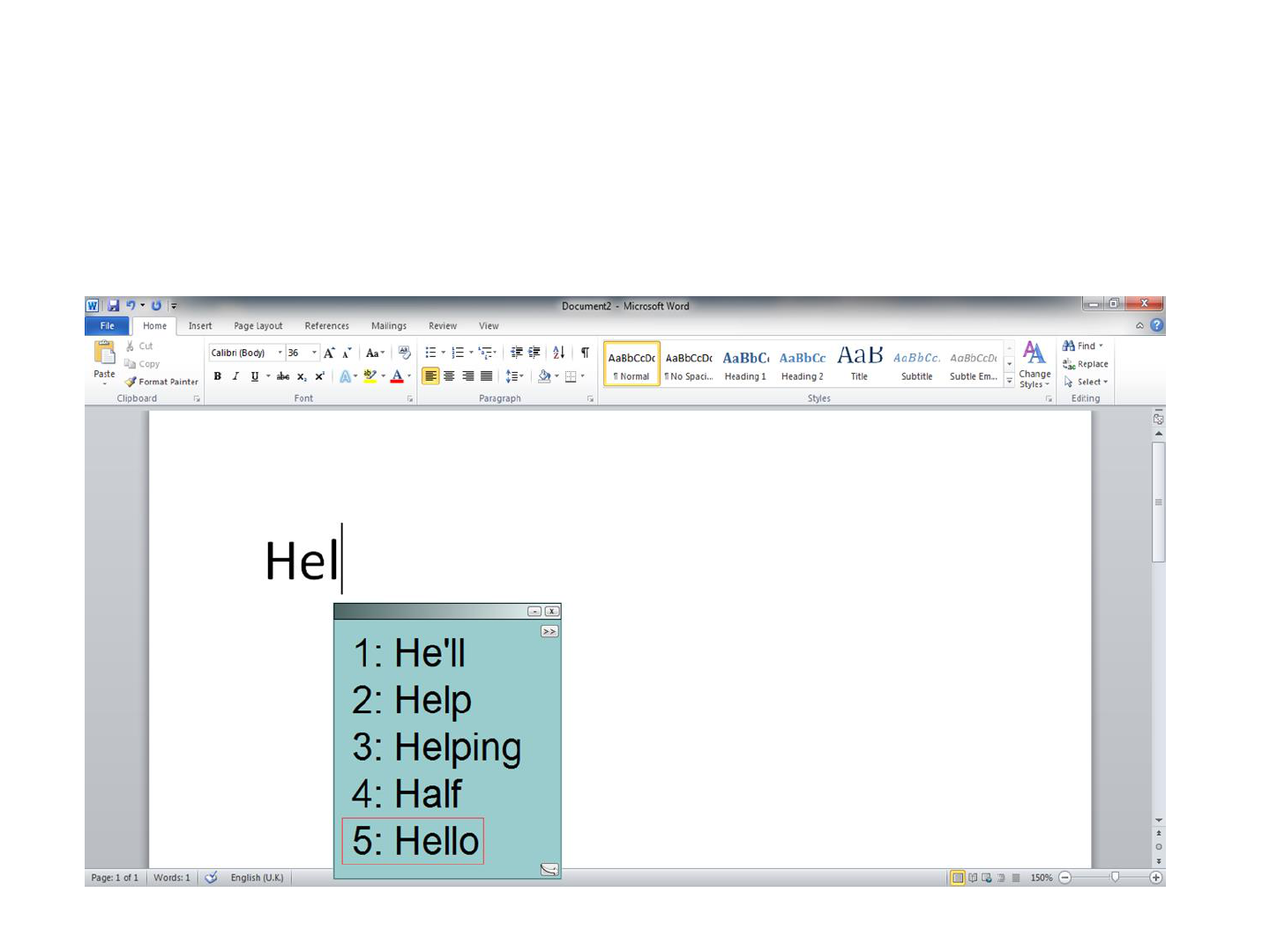
Co:Writer 7 (Don Johnston Technologies)
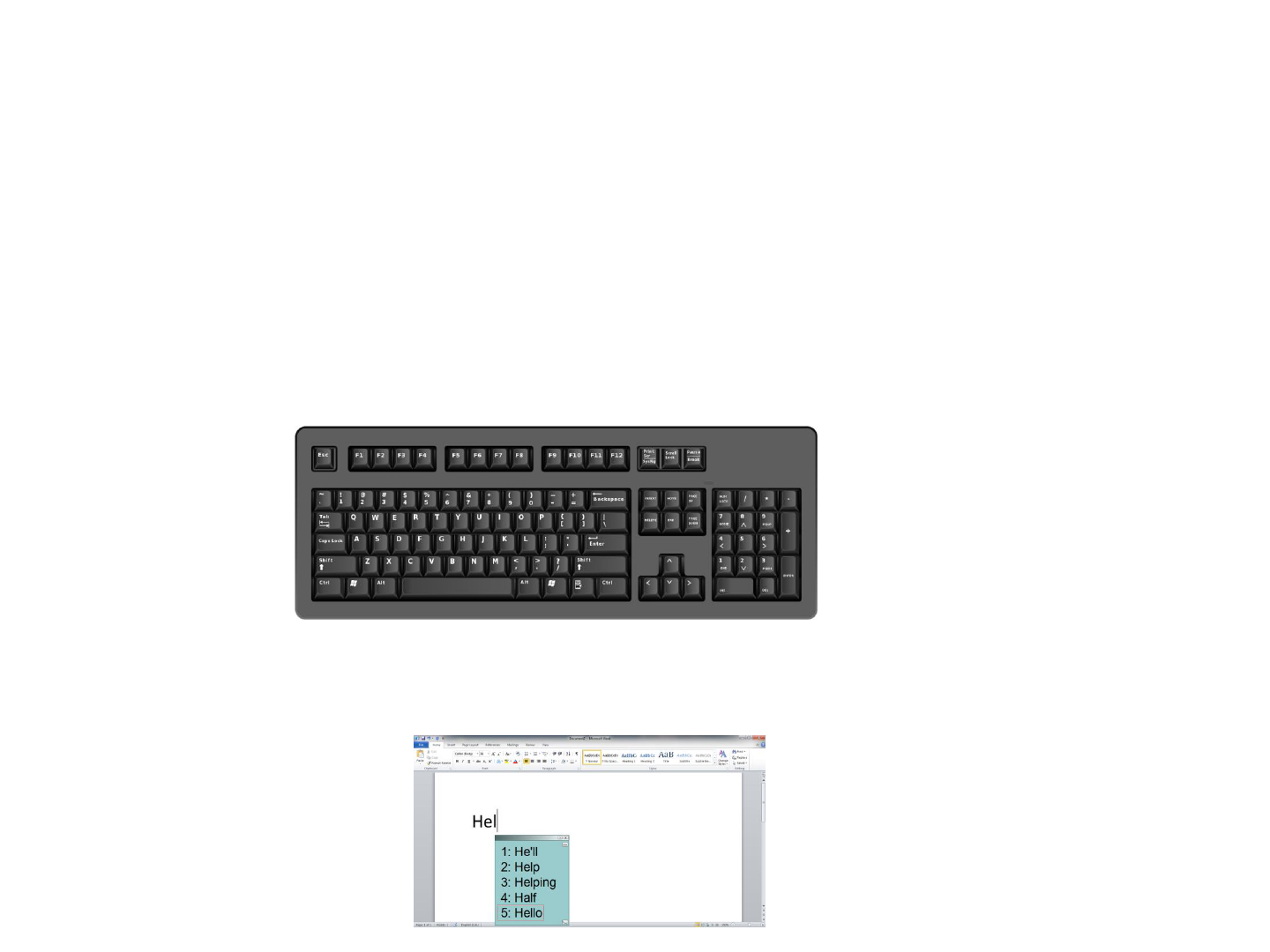
Word prediction
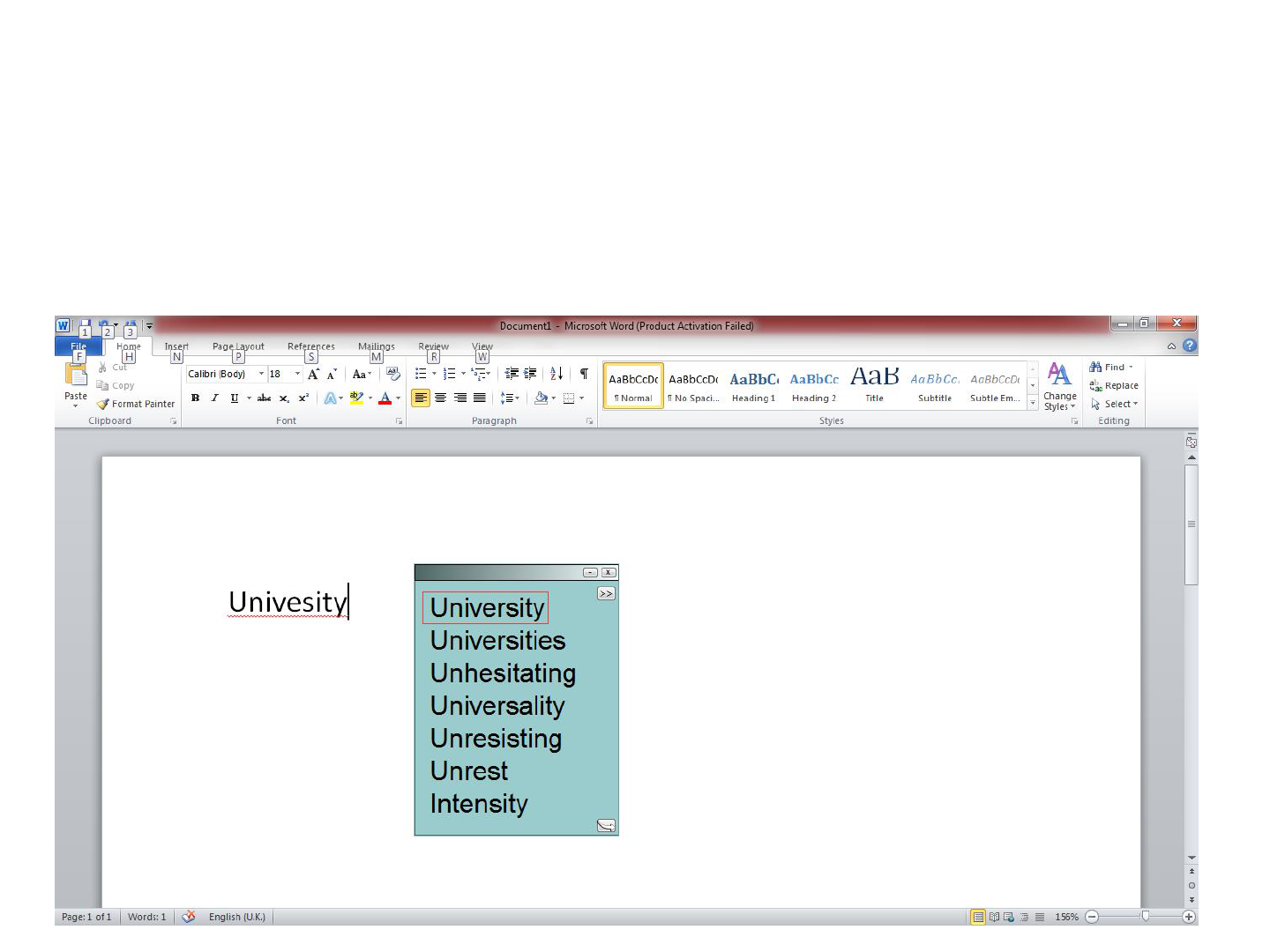
Co:Writer 7
Spell check
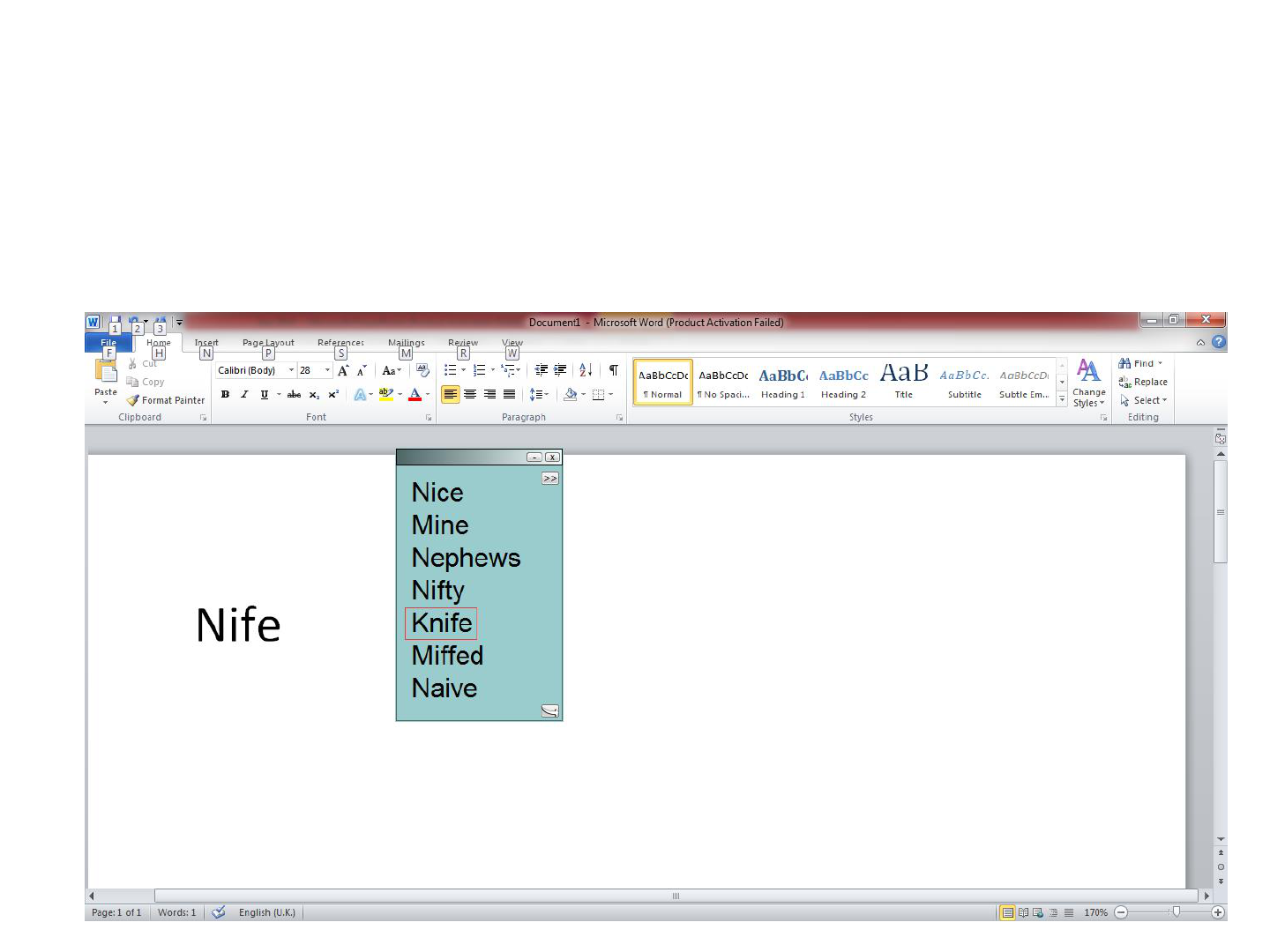
Co:Writer 7
Sensitive to regularisation errors
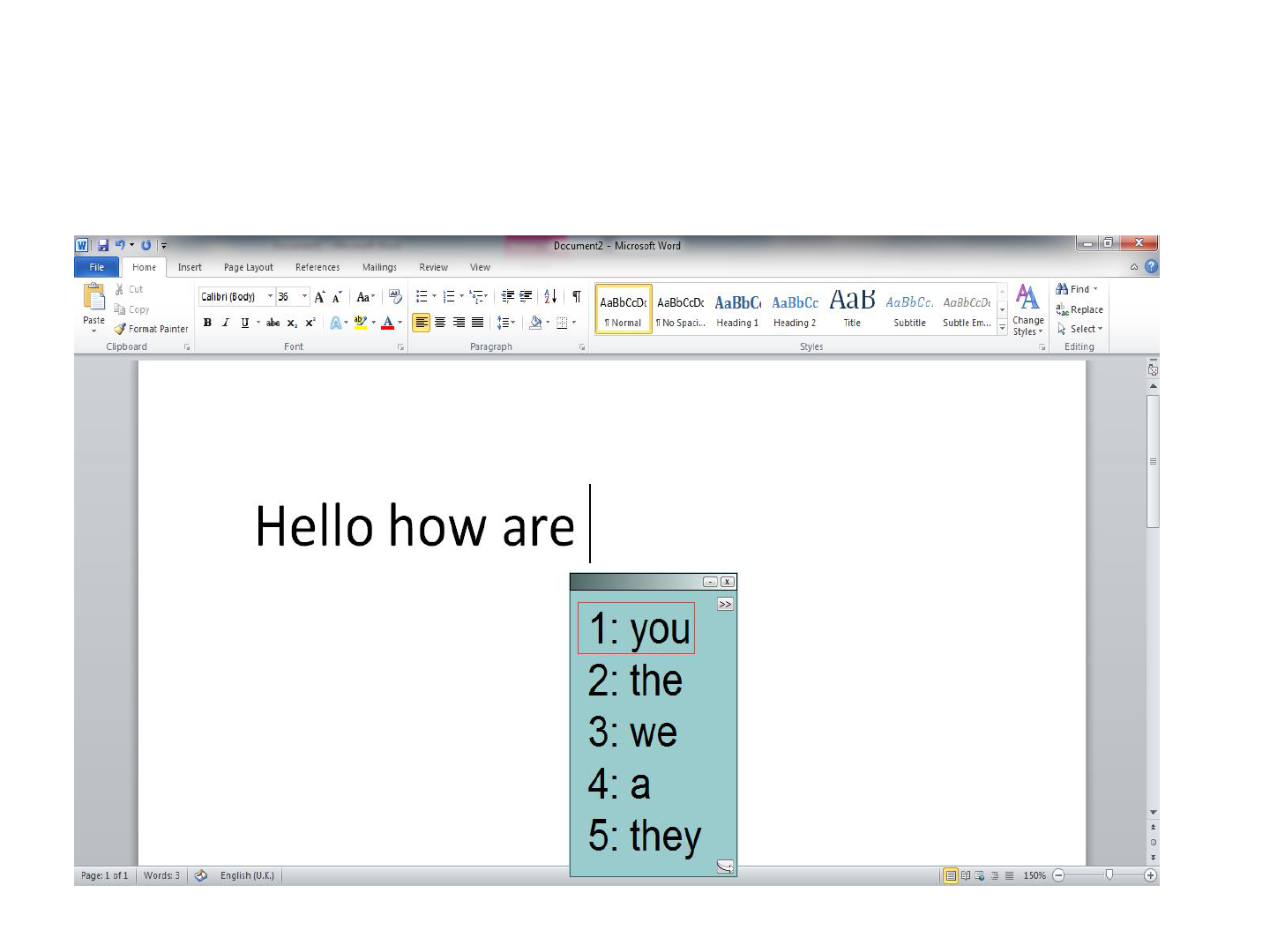
Co:Writer7
Grammar prediction
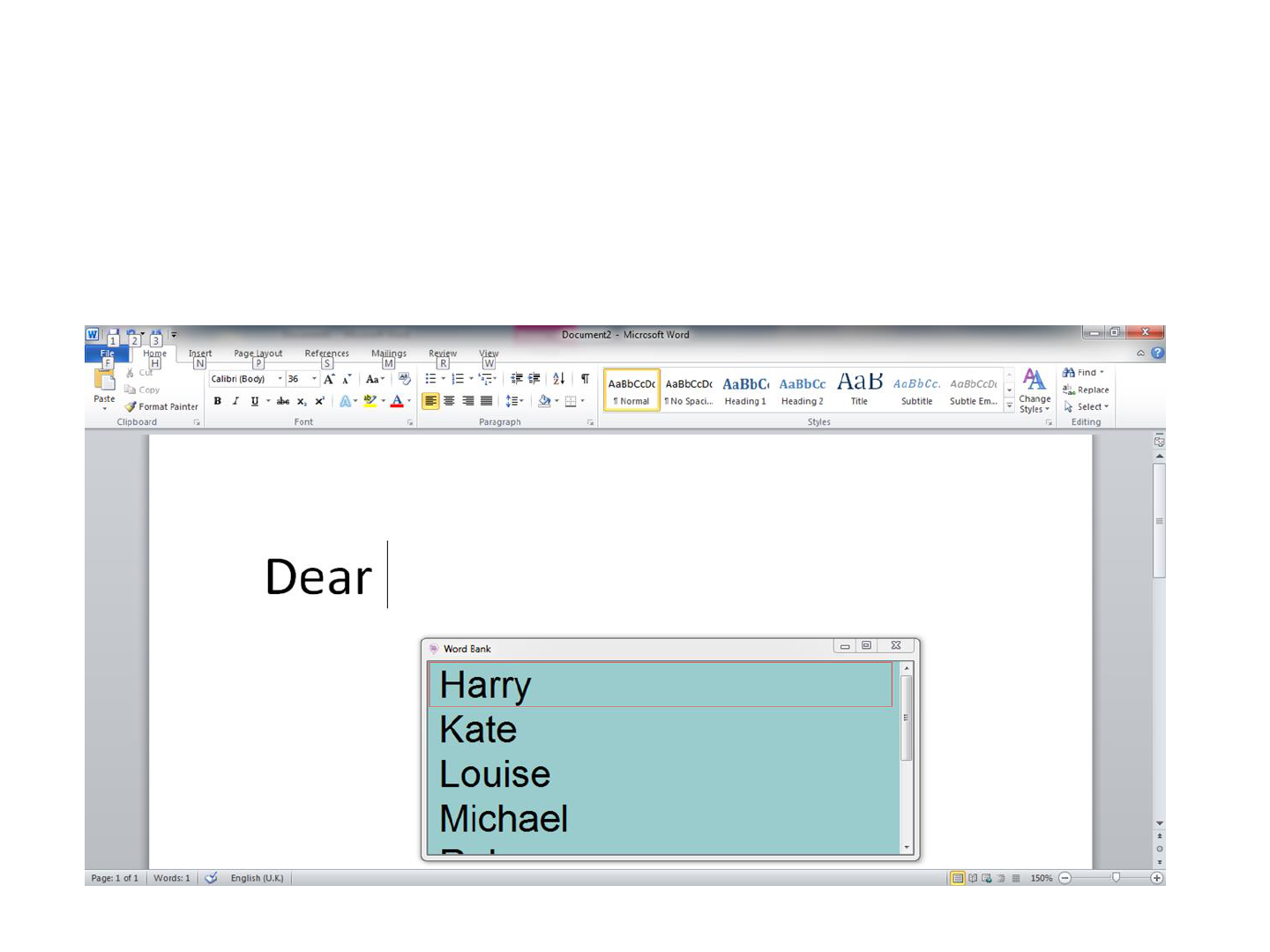
Co:Writer 7
Word/ phrase banks
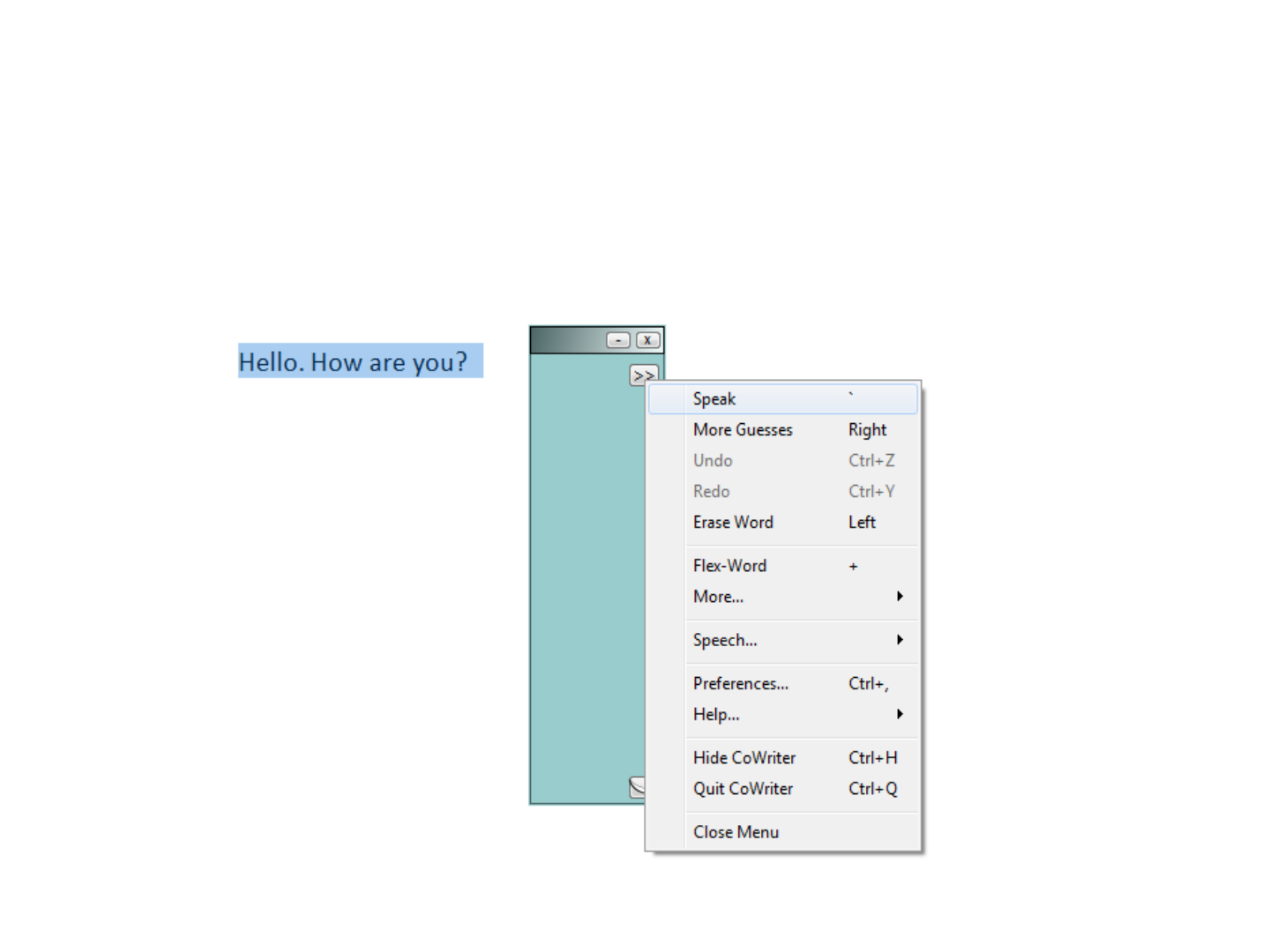
Co:Writer 7
Text to speech
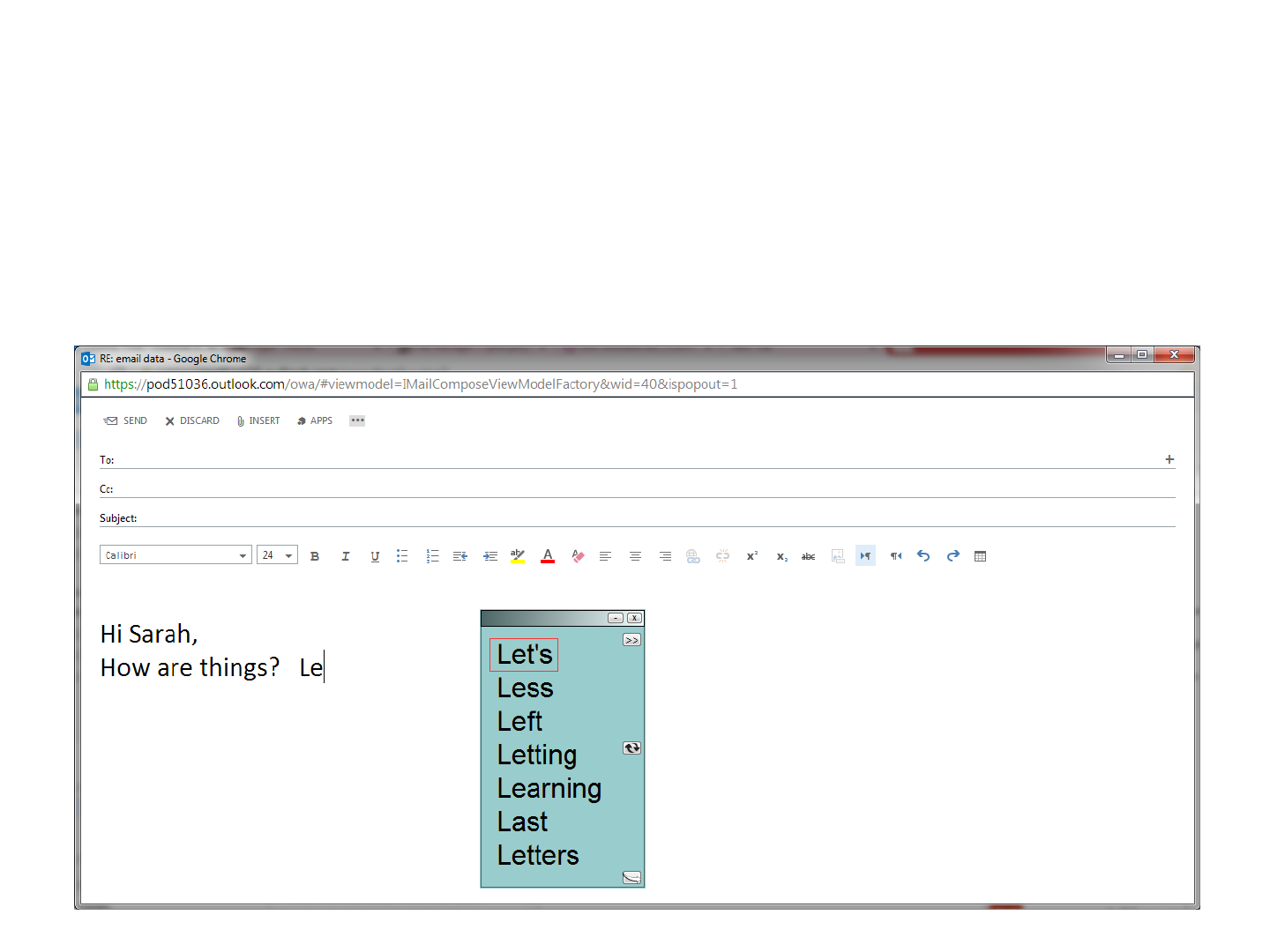
Co:Writer 7
Can use online (e.g. email, Facebook, Skype) – in theory!
Therapy protocol
x10 - 1 hour sessions over 5 weeks
Each therapy session consisted of
• Technology access training (0-15 minutes)
• Writing with Co:Writer (45-60 minutes)
Technology Access Training
Keyboard practice: copying short texts
Email training:
1. Turn on the computer
2. Open your email account
3. Create a new message, enter an e-mail and send a blank e-mail.
4. Send an e-mail with an attachment
5. Send an e-mail with a subject entered
6. Reply to an e-mail in your inbox
7. Enter an addressee into the cc box
8. Forward an e-mail
Finish when each task has been completed independently x3
Writing with Co:Writer
Session
Topic
Level
1
Introduction
& orientation
2
Writing
for domestic needs
Simple
tasks
3
Writing
for social needs
Simple
tasks
4
Writing
for business/ administrative needs
Simple
tasks
5
Writing
for domestic needs
Medium
complexity
6
Writing
for social needs
Medium
complexity
7
Writing
for business/ administrative needs
Medium
complexity
8
Writing
for domestic needs
High
complexity
9
Writing
for social needs
High
complexity
10
Writing
for business/administrative needs
High
complexity
Write a birthday card to a friend
Instructions to your neighbour, explaining
what they need to do in your house while
you’re on holiday.et).
Write to a charity/ organisation/
company explaining why you would
like to work/ volunteer for them and
why they should employ you

General principles
• At beginning of session entered words and phrases into word
banks together
• Encouraged to use word bank, prediction, text to speech and
spell check to complete tasks
• Participants completed tasks as independently as possible
• Could ask for therapist’s help (modelling, instructions)
whenever necessary
• Possible 3 tasks to complete per session, but worked through
at own pace
• Continued to next topic/ difficulty level in next session.
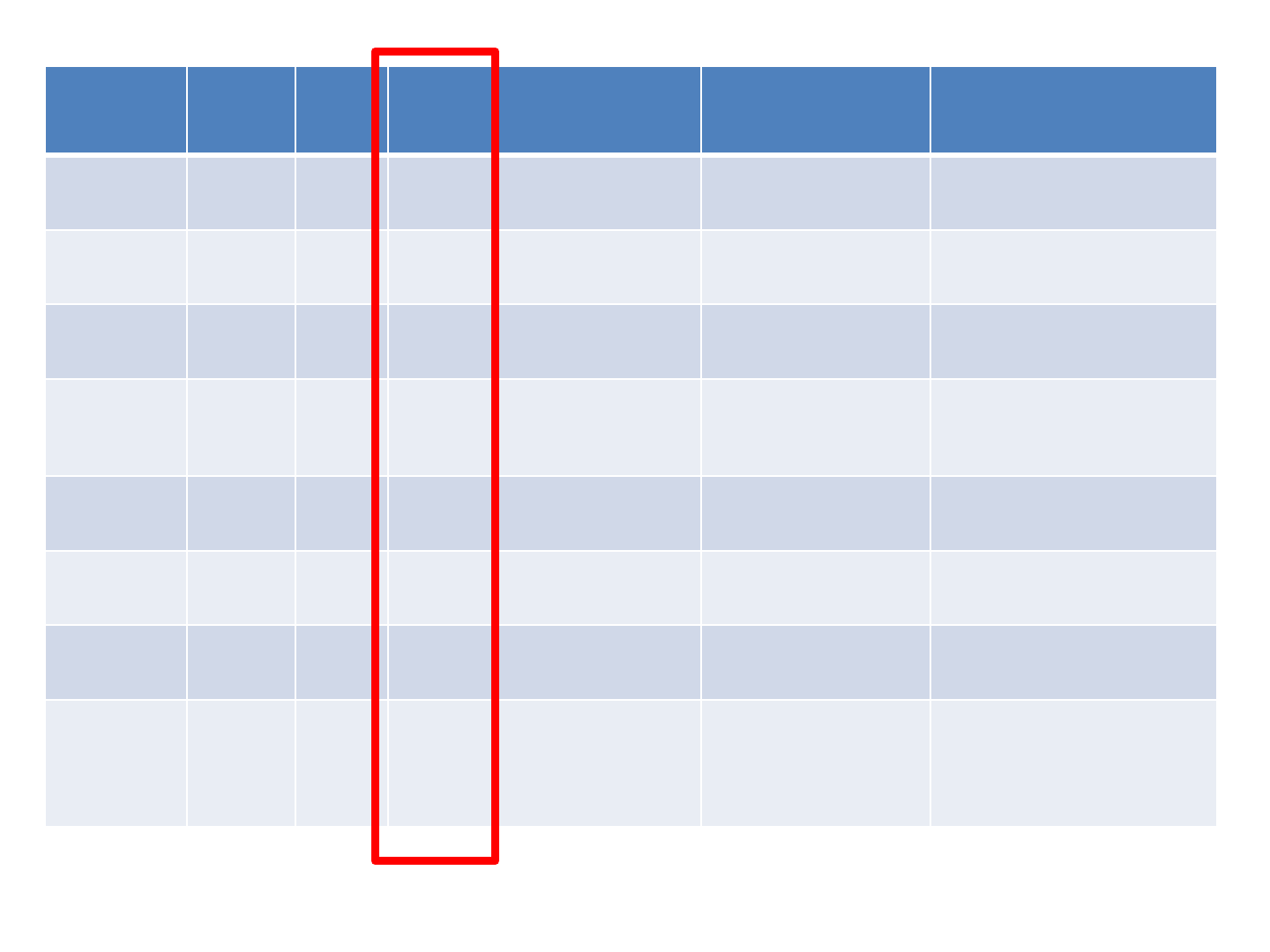
Age
Ed.
LR/R
H
Time since
CVA
Aphasia
Dysgraphia
LR
66
11
RH
19
years
Anomic
GBD
GP
58
12
RH
3 years
Non
-fluent
Phonological
DM
50
16
RH
7 years
Non
-fluent
Phonological/deep
KR
58
11
RH
6 years
Non
-fluent
Deep
AD
74
11
RH
5 years
Conduction
GBD
JB
80
9
RH
19 years
Non
-fluent
GBD
SR
47
10
RH
4 years
Recovered
Surface
EB
50
10
RH
4 years
Fluent with
phonological
errors
GBD
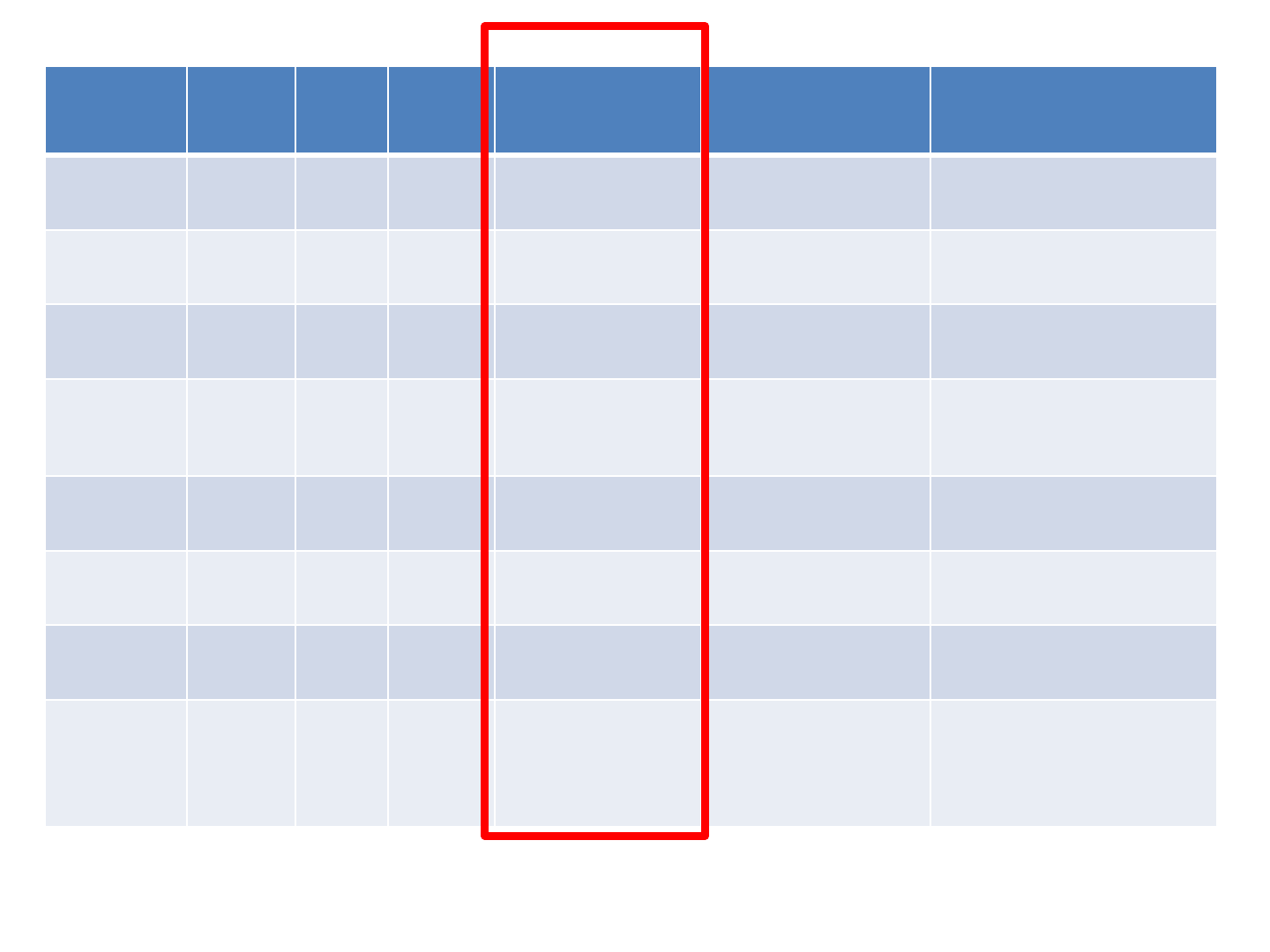
Age
Ed.
LR/R
H
Time since
CVA
Aphasia
Dysgraphia
LR
66
11
RH
19
years
Anomic
GBD
GP
58
12
RH
3 years
Non
-fluent
Phonological
DM
50
16
RH
7 years
Non
-fluent
Phonological/deep
KR
58
11
RH
6 years
Non
-fluent
Deep
AD
74
11
RH
5 years
Conduction
GBD
JB
80
9
RH
19 years
Non
-fluent
GBD
SR
47
10
RH
4 years
Recovered
Surface
EB
50
10
RH
4 years
Fluent with
phonological
errors
GBD
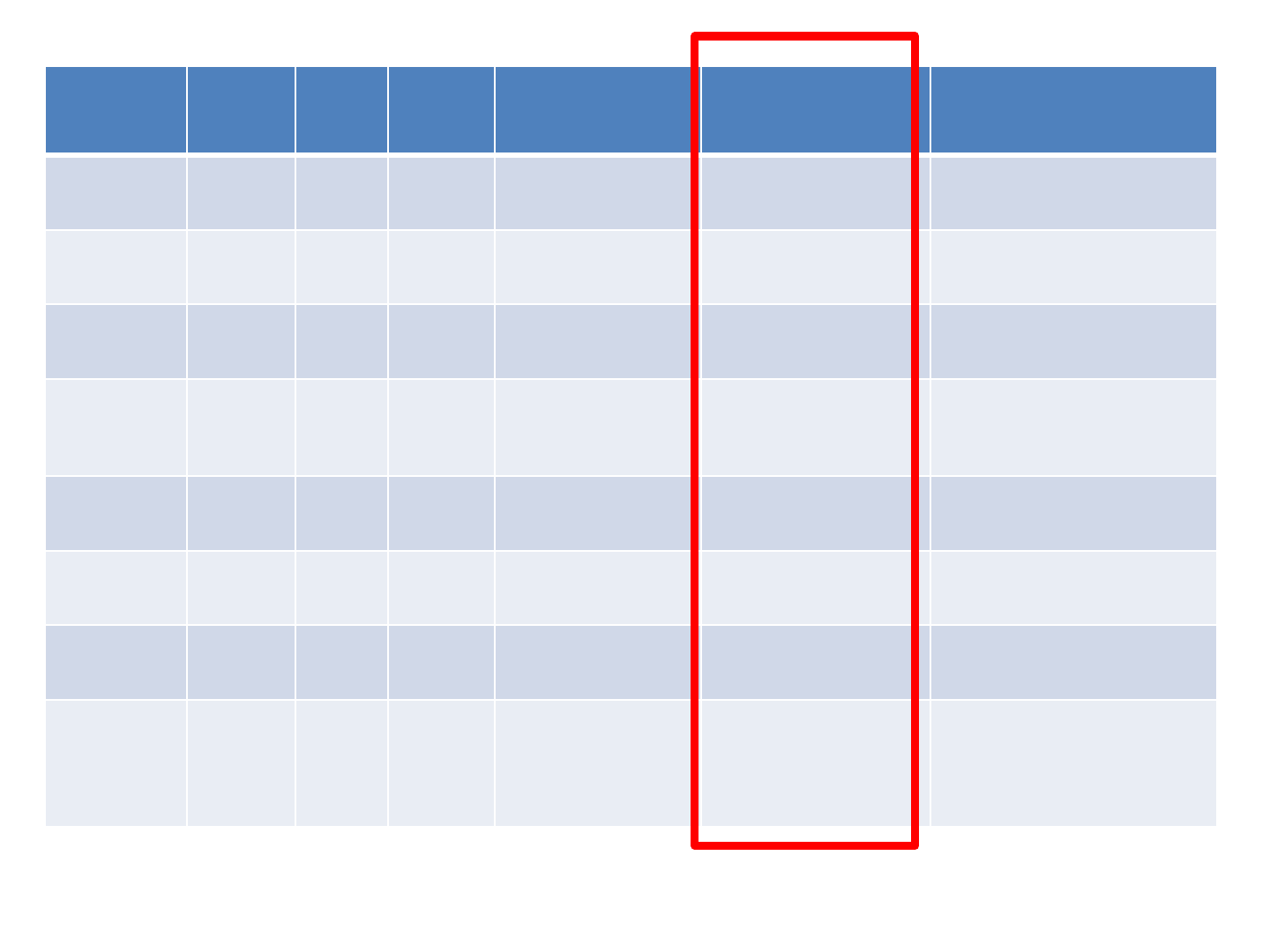
Age
Ed.
LR/R
H
Time since
CVA
Aphasia
Dysgraphia
LR
66
11
RH
19
years
Anomic
GBD
GP
58
12
RH
3 years
Non
-fluent
Phonological
DM
50
16
RH
7 years
Non
-fluent
Phonological/deep
KR
58
11
RH
6 years
Non
-fluent
Deep
AD
74
11
RH
5 years
Conduction
GBD
JB
80
9
RH
19 years
Non
-fluent
GBD
SR
47
10
RH
4 years
Recovered
Surface
EB
50
10
RH
4 years
Fluent with
phonological
errors
GBD
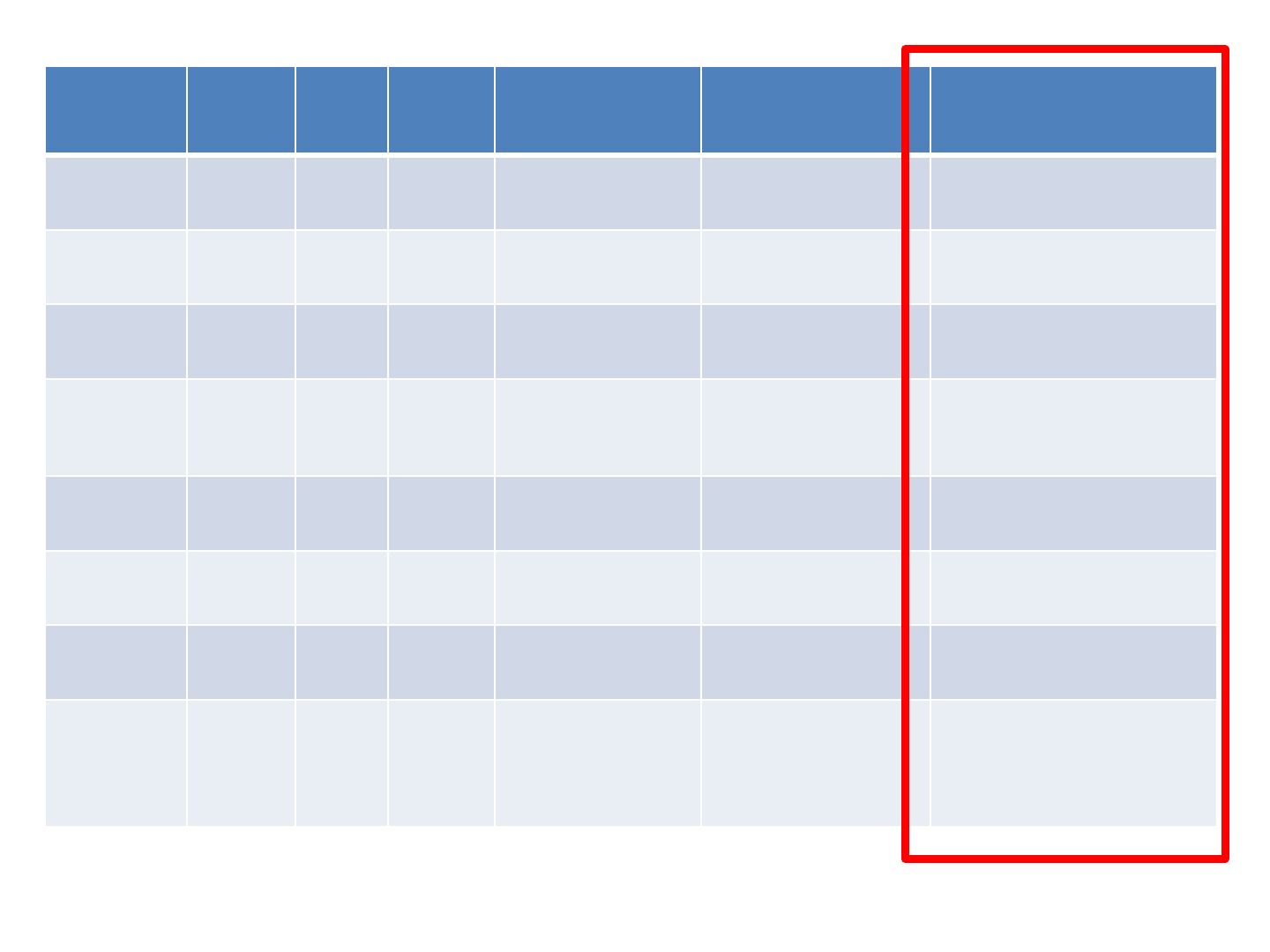
Age
Ed.
LR/R
H
Time since
CVA
Aphasia
Dysgraphia
LR
66
11
RH
19
years
Anomic
GBD
GP
58
12
RH
3 years
Non
-fluent
Phonological
DM
50
16
RH
7 years
Non
-fluent
Phonological/deep
KR
58
11
RH
6 years
Non
-fluent
Deep
AD
74
11
RH
5 years
Conduction
GBD
JB
80
9
RH
19 years
Non
-fluent
GBD
SR
47
10
RH
4 years
Recovered
Surface
EB
50
10
RH
4 years
Fluent with
phonological
errors
GBD
Age
Ed.
LR/R
H
Time since
CVA
Aphasia
Dysgraphia
LR
66
11
RH
19
years
Anomic
GBD
GP
58
12
RH
3 years
Non
-fluent
Phonological
DM
50
16
RH
7 years
Non
-fluent
Phonological/deep
KR
58
11
RH
6 years
Non
-fluent
Deep
AD
74
11
RH
5 years
Conduction
GBD
JB
80
9
RH
19 years
Non
-fluent
GBD
SR
47
10
RH
4 years
Recovered
Surface
EB
50
10
RH
4 years
Fluent with
phonological
errors
GBD
Age
Ed.
LR/R
H
Time since
CVA
Aphasia
Dysgraphia
LR
66
11
RH
19
years
Anomic
GBD
GP
58
12
RH
3 years
Non
-fluent
Phonological
DM
50
16
RH
7 years
Non
-fluent
Phonological/deep
KR
58
11
RH
6 years
Non
-fluent
Deep
AD
74
11
RH
5 years
Conduction
GBD
JB
80
9
RH
19 years
Non
-fluent
GBD
SR
47
10
RH
4 years
Recovered
Surface
EB
50
10
RH
4 years
Fluent with
phonological
errors
GBD
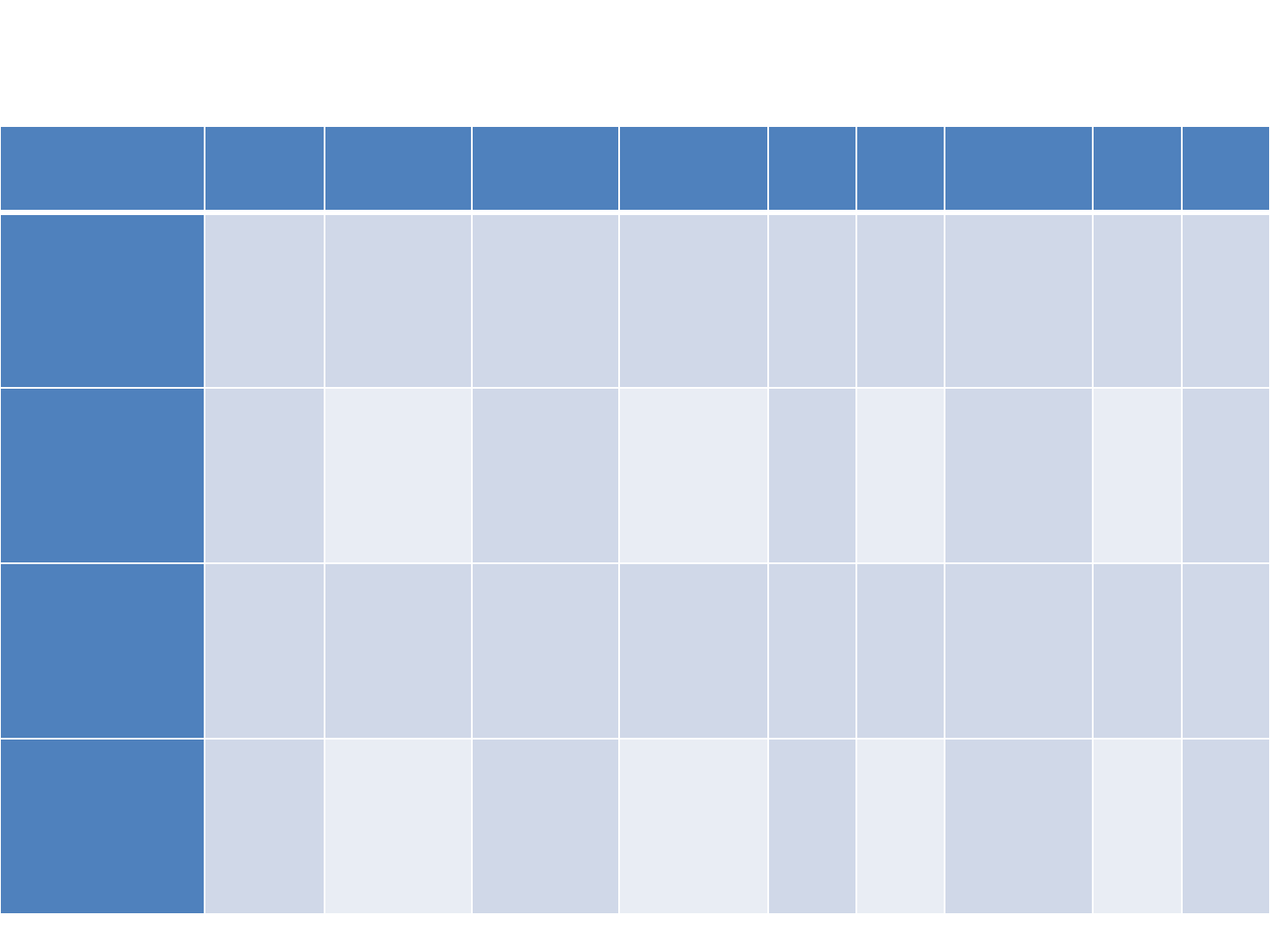
Baseline CAT writing scores
Participants:
LR
GP
DM
KR
AD
JB
SR
EB
CAT Scores (no.
letters correct)
Copying
27/27
27/27
27/27
27/27
25/27
26/27
27/27
27/27
Written
picture
naming
7/21
13/21
19/21
17/21
13/21
17/21
18/21
18/21
Writing
to
dictation
12/28
5/28
17/28
6/28
13/28
16/28
26/28
24/28
Written
picture
descripti
on
3
6
2
15
4
1
8
22

Results
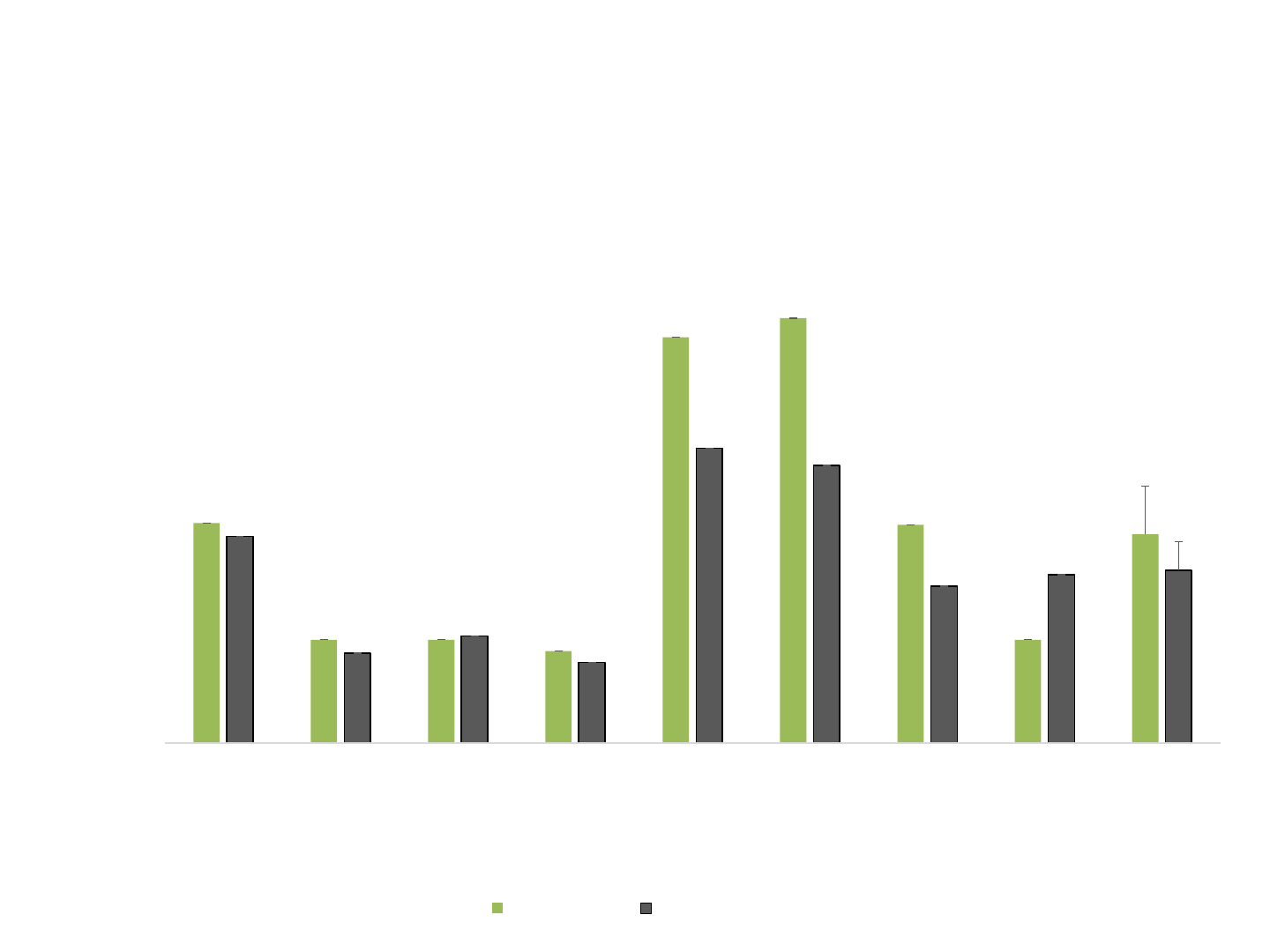
• Across all 3 emails : Tasks 1, 2 and 3 collapsed
• Time limit 3 minutes for each email – 9 minutes total
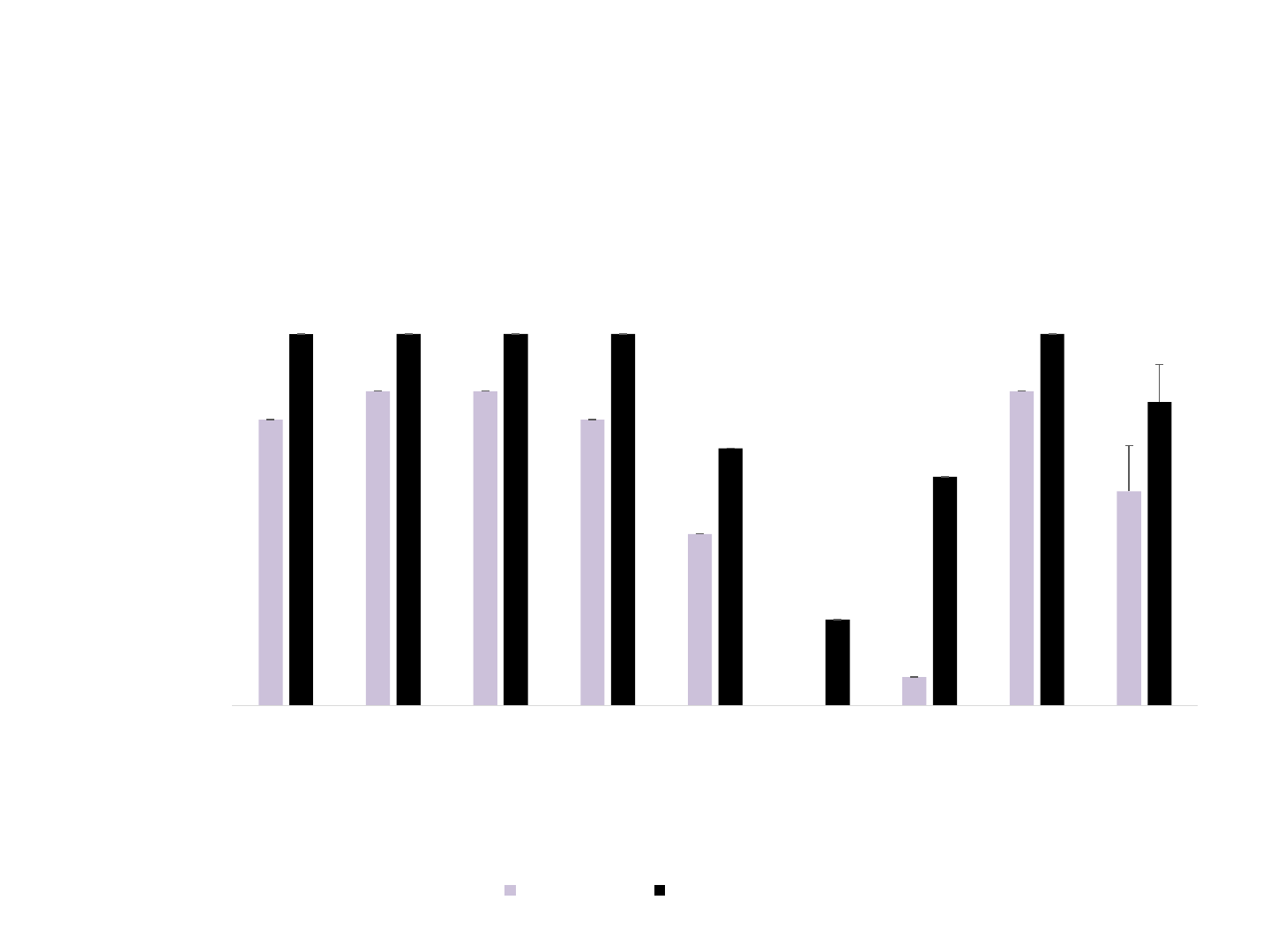

Number of tasks completed independently in the
Internet Skills Assessment
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
LR GP DM KR AD JB SR EB Mean
Number of tasks completed
independently
Participant
Figure 1. Number of tasks completed independently in the Internet
Skills Assessment
Pre therapy Post therapy
*
*
*
p < .05
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
LR GP DM KR AD JB SR EB Mean
Number of tasks completed independently
Participant
Pre therapy Post therapy
*
*
*
p < .05
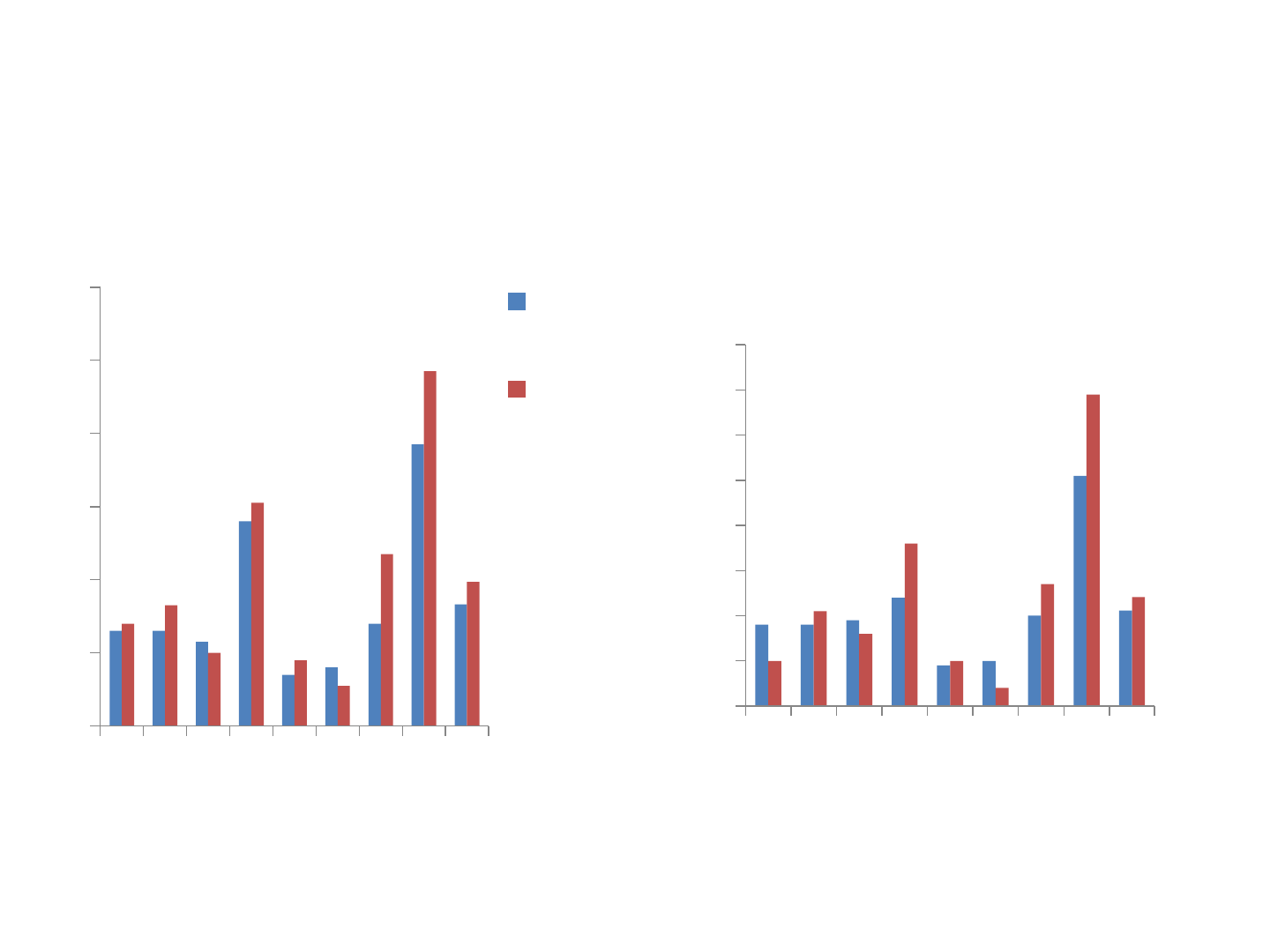
Speed of typing within Keyboard Skills
Assessment
0
5
10
15
20
25
LR GP DM KR AD JB SR EB Mean
Number of minutes for all tasks
Participant
Pre therapy Post therapy
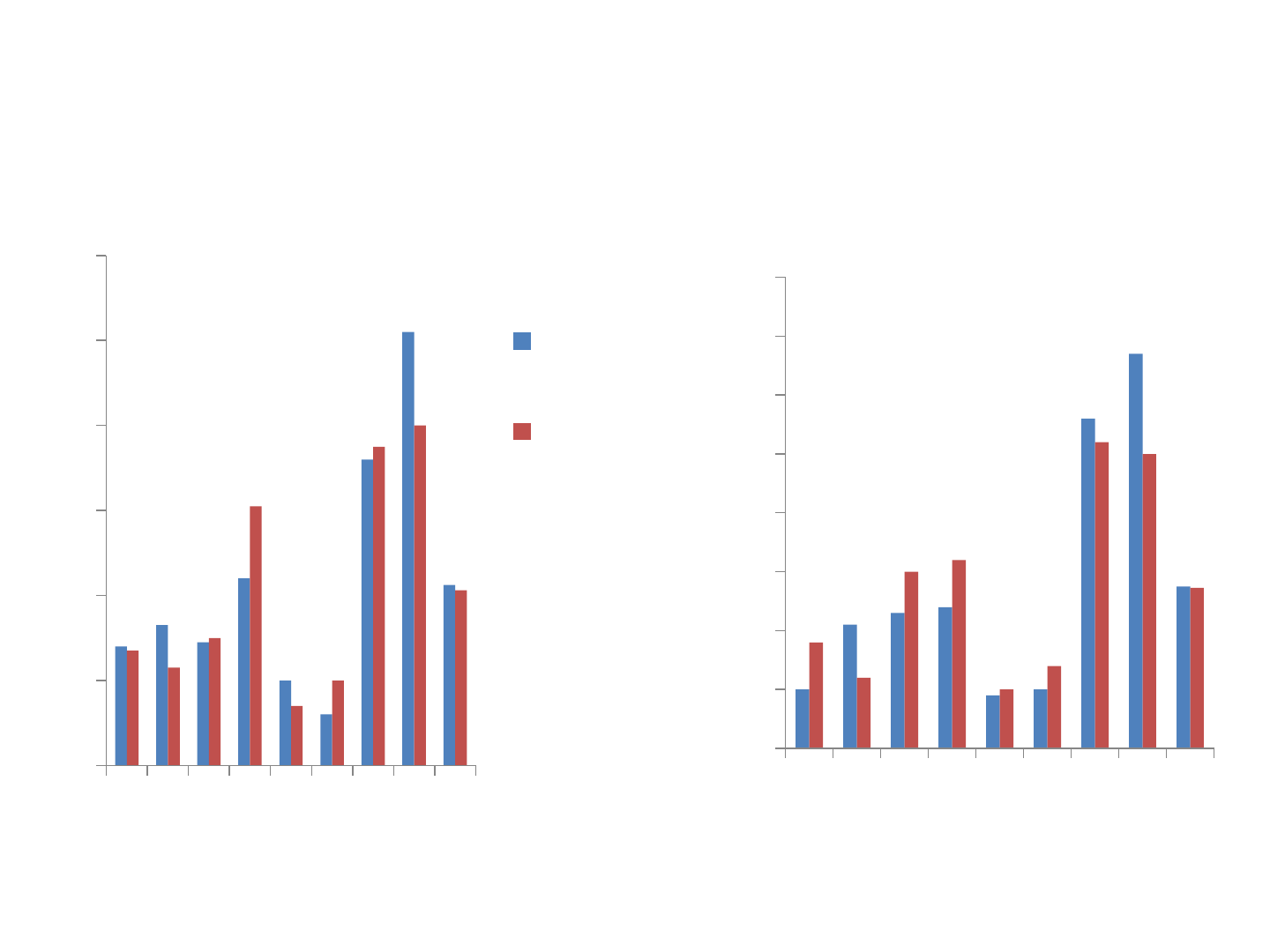
Effort Phase
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
LR
GP
DM
KR
AD
JB
SR
EB
Mean
Pre effort
phase
Post effort
phase
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
LR
GP
DM
KR
AD
JB
SR
EB
Mean
Does email writing improve with effort alone?
Correct units per minute Correct and informative units per minute
Writing without Co:Writer
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
LR
GP
DM
KR
AD
JB
SR
EB
M…
Pre therapy
Post therapy
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
LR
GP
DM
KR
AD
JB
SR
EB
M…
Correct units per minute Correct and informative units per minute
Are there any general improvements to email writing without using
Co:Writer?
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
LR GP DM KR AD JB SR EB Mean
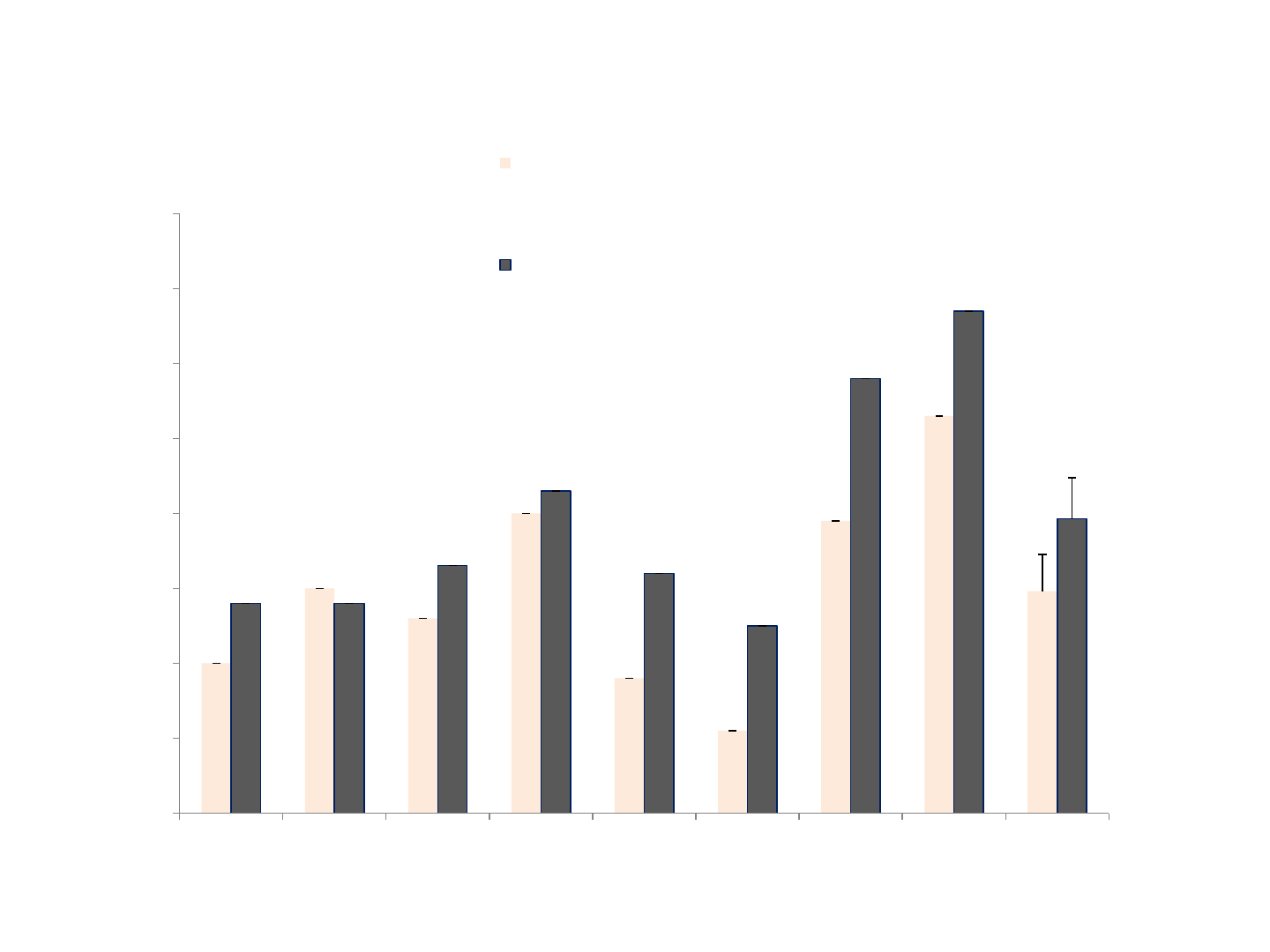
Correct units
Participant
Number of correct units pre therapy without Co:writer
compared to post therapy with Co:Writer
pre therapy without
Co:Writer
post therapy with Co:Writer
*
*
*
* p < .05
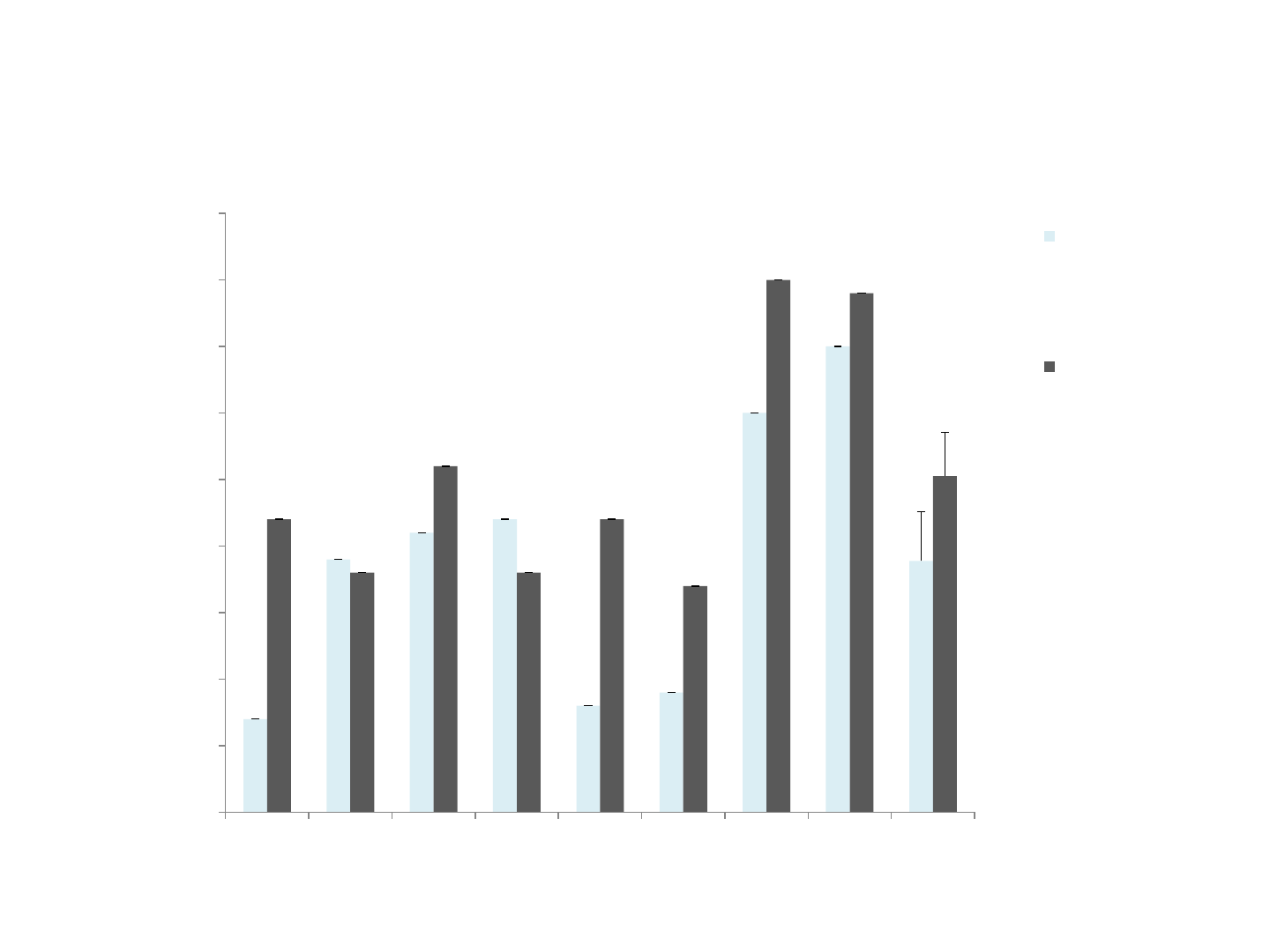
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
LR GP DM KR AD JB SR EB Mean
Correct and informative units
Participant
Number of correct and informative units pre therapy
without Co:Writer compared to post therapy with Co:Writer
pre therapy without
Co:Writer
post therapy with
Co:Writer
*
*
*
*p < .05
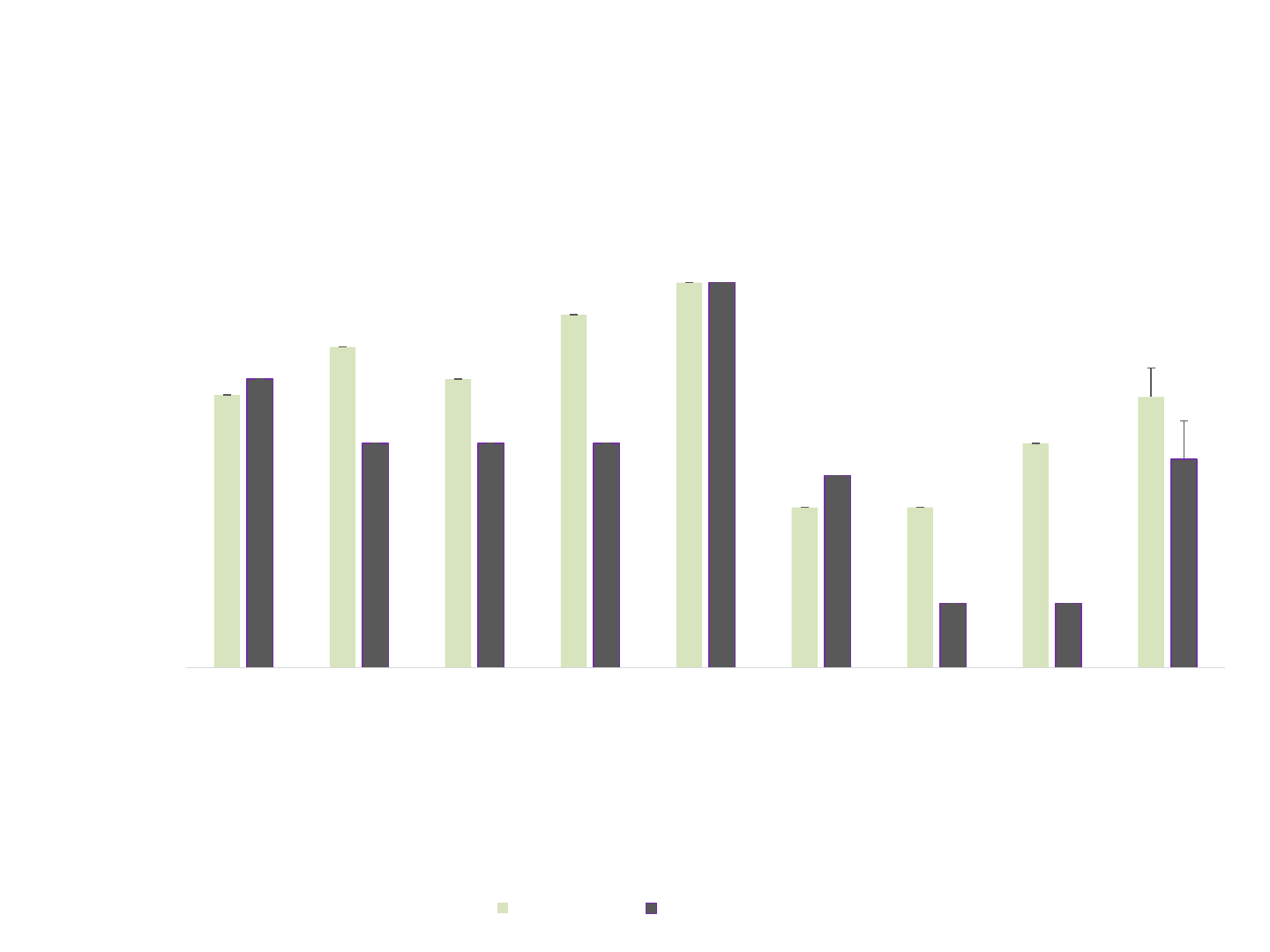
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
LR GP DM KR AD JB SR EB Mean
Rating
Participant
CAT Disability Questionnaire:
Ratings on writing subtest
Pre therapy Post therapy
*
*p < .05
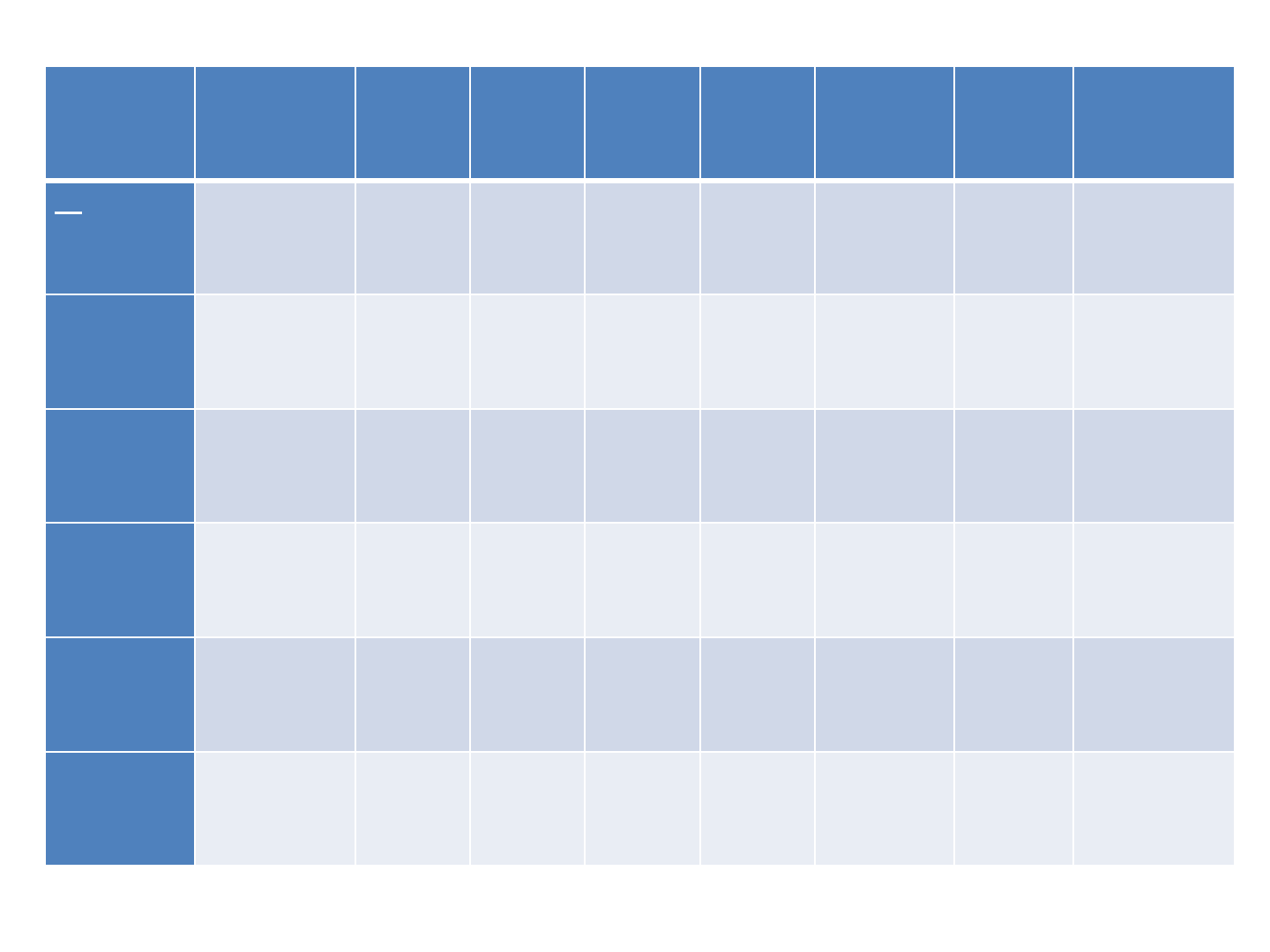
Proportion (%) of each word class in pre and post therapy emails
Participant
N
V
Adj
Adv
Exclam
Num
Function
LR
Pre
13
.6
13
.6
-
-
-
4
.5
68
.2
Post
25
21
.4
14
.3
3
.6
3
.6
-
32
.1
DM
Pre
75
-
16
.7
-
4
.2
4
.2
-
Post
50
3
.1
18
.8
3
.1
6
.3
9
.4
6
.2
AD
Pre
11
.1
11
.1
11
.1
-
-
-
66
.7
Post
6
.8
22
.7
9
.1
13
.6
-
-
47
.7

Summary
Engaging in this treatment programme meant that:
o participants became more independent though not faster in
internet skills
o Effort and non-use of the compensatory technology showed
no gains for email writing
o Group level gains in correct words and correct/informative
words with compensatory technology, some greater variety of
word classes used
o This effects were carried by half of the participants
o Perceived impact on functional writing skill

Factors affecting individual variation
Cog/ ling
Prior use
Spelling type/ severity
Motivation
Ease of use of technology

Future directions
Investigation of relationships between performance on
cognitive/ language/ spelling assessments and outcomes
Prescriptive intervention – what should work best for you
is…..
Interviews and analysis of interview data
Aphasia-friendly app
Literacy focus - combined reading & writing package
Quality of written language production

• Thiel, L., Sage, K. & Conroy, P. (2013). Comparing uni-modal and
multi-modal therapies for improving writing in acquired dysgraphia.
Poster presented at the British Aphasiology Society Biennial
International Conference 2013, University of Manchester.
• Thiel, L., Sage, K. & Conroy, P. (2013). Combining word learning
therapies and computer technologies to improve writing in people
with aphasia. Paper presented at the Speakeasy Annual Conference,
Bury, Greater Manchester.
• Thiel, L., Sage, K. & Conroy, P. (2014). The role of learning in
promoting functional writing. Poster presented at the 16th
International Aphasia Rehabilitation Conference 2014, The Hague,
The Netherlands.
• Thiel, L., Sage, K. & Conroy, P. (2014). Training people with aphasia
to use word prediction software for email writing. Paper presented
at the British Aphasiology Society Therapy Symposium, Birmingham
City University.
• Thiel, L., Sage, K. & Conroy, P. (2015). Retraining writing for
functional purposes: a review of the writing therapy literature.
Aphasiology, 29(4), 423-441.

Discussion
DM, EB and GP
• Did not improve significantly;
• What do they have in common?
– All mastered Co:Writer very quickly, enjoyed using it and wrote well
within therapy. DM and EB continued using after therapy.
– Were writing emails before and during study
– Good cognitive skills
• Possible reasons for no improvements
– Chose to use predictive writing more than word banks = slow to use
and don’t see such large improvements in correct words per minute
– Assessment not sensitive to change

Discussion
AD, JB and LR
• All improved significantly when using Co:Writer post therapy
• What do they have in common?
– Severely impaired spelling; graphemic buffer disorder
– Severely impaired email writing and dependent on support
– Severely impaired cognitive skills (executive functioning; visual memory)
• In what way did Co:Writer help them?
– All relied on word/ phrase bank function – one click produces multiple
words.
– However, all have extreme difficulties in using Co:Writer (found it
frustrating) within therapy and none used Co:Writer independently after
therapy
